-

Tissue-Engineered Delivery of Manuka Honey
Calista Adler, Karina Mitchell, Sreejith Panicker, and Katherine R. Hixon
Manuka Honey (MH) contains the Unique Manuka Honey Factor (UMF), which is directly correlated to honey’s antibacterial efficiency and has a wide range of wound healing properties. In more recent years, MH has been incorporated into tissue-engineering scaffolds including cryogels, hydrogels, electrospun fibers, and electrosprayed nanoparticles. Tissue-engineered scaffolds can serve as alternative vehicles for delivery as compared to traditional wound dressings.The project objective was to investigate which of the four scaffold types can successfully incorporate MH (0, 1, 5, 10%) while retaining original parameters. We hypothesize that cryogels offer the best vehicle of delivery of MH because of increased durability (mechanical properties) compared to that of hydrogels and electrospun/electrosprayed scaffolds.
-
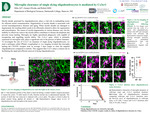
Microglia clearance of single dying oligodendrocytes is mediated by Cx3cr1
Hiba Ali, Genaro E. Olveda, and Robert Hill
Myelin sheath, generated by oligodendrocytes, plays a vital role in ensheathing axons for efficient neural communication. Degeneration of myelin sheath is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases and aging. When myelin sheaths are damaged or degenerated, the resulting debris needs to be efficiently cleared to allow for regeneration and remyelination. The causes of myelin degeneration in various diseases vary, but the inability to effectively remove the myelin debris contributes to disease development and prevents tissue healing. Microglia are highly specialized phagocytic cells capable of recognizing and engulfing myelin debris. The Cx3cr1 gene, which is primarily expressed on microglial cells, plays a significant role in the process of debris clearance. To investigate the role of Cx3cr1 on clearance of single dying oligodendrocytes, we used a technique called 2Phatal. Longitudinal in vivo imaging revealed that microglia lacking the CX3CR1 receptor took on average 3 days longer to clear the targeted oligodendrocytes compared to controls. This suggests that Cx3cr1 plays a critical role in facilitating the rapid and efficient removal of dying oligodendrocytes.
-

Flicker-induced geometric hallucinations: VEP and plasticity correlates
Grace Beilstein, Peter Tse, Nathan Heller, and Nisha Patel
This experiment expores the link between neuroplasticity and induced hallucinations. With the stroboscopic stimulation model, we induced frequency-dependent hallucination. Using EEG, we compared visually-evoked potentials (VEPs) from occipital electrode recordings. We used these VEP recordings as an indicator of attentional allocation and responsiveness to the stimulus. We are contributing to the body of work involving halllucination-inducing models by exploring the relationship to plasticity.
-

On the origins of crenarchaeol: environmental controls on an enigmatic archaeal lipid in hot springs
Amanda Calhoun, Jerome Blewett, Daniel Colman, Carolynn Harris, Eric Boyd, Ann Pearson, and William Leavitt
Glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers (GDGTs) are membrane-spanning lipids of archaea that are ubiquitous in hot spring, ocean, lake, and soil environments. These lipids allow for microbial acclimatization to environmental stress and serve as the basis for important paleotemperature proxies. The number of cyclopentyl rings in the core structure of archaeal GDGTs change in response to temperature, pH, and oxidant load in both environmental samples and in cultured marine and acidophilic hot spring strains. Archaea from acidic hot springs can produce GDGT moieties with up to eight cyclopentyl rings (GDGT-0 to -8). Biophysical models show that synthesizing more cyclopentyl rings promotes tighter membrane packing and decreased permeability, enabling archaea to occupy hotter, more acidic, and more oxidizing environments. A unique GDGT found in both marine and hot spring archaea, crenarchaeol, contains four cyclopentyl and one cyclohexyl ring. While the function of this lipid in archaeal membranes is not well understood, it has been proposed that the cyclohexyl ring allowed archaea adapted to acidic, high temperature hot springs to adapt to cooler and circumneutral waters, eventually allowing for diversification into oceanic environments. To improve the understanding of crenarchaeol’s function in membranes, its role in archaeal evolution, and its distribution in the geologic record, we quantify the relationship between pH, temperature, redox, and other parameters with crenarchaeol abundance in the natural thermal springs of Yellowstone National Park, where these parameters vary widely. We evaluate our data in the context of a comprehensive compilation of previously reported GDGT data from hot spring environments, focusing particularly on crenarchaeol, to examine the environmental factors that likely control its distribution. These results shed new light on the role of crenarchaeol in the diversification of archaea into lower temperature, circumneutral environments.
-

Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Recycled Polymer Interfaces
Mariana I. Cepeda, Lingyi Zou, and Wenlin Zhang
For this project, we carried out large-scale, long-time Molecular Dynamics (MD) united-atom simulations of pure polyethylene and polypropylene, subsequently bringing them together to resemble the blends seen in most recycled plastics. We then observed the phase separation in the melt state and exhibited stable interfaces between the two polymers. The study lays a basic foundation for future study of crystallization and mechanical properties of polyethylene/polypropylene plastic blends.
-

Dynamic Nuclear Polarization in Diamond
Catherine Chu and Chandrasekhar Ramanathan
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) is a technique used to amplify the signal in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). Magnetic resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when spins in a magnetic field are excited by a resonant electromagnetic field. In our experiment, we apply a radio-frequency (RF pulse) to the nucleus of a sample at the same frequency that the nuclear spin is precessing.
-

Investigating URI Targets in Arabidopsis Thaliana in Shoot Tissue Under Iron Sufficient or Deficient Conditions
Paget Eleanor Chung, Fiona Belbin, and Mary Lou Guerinot
-

Subcellular localization impacts PTEN activity in the murine dentate gyrus
Nicole Desmet, Annaliese OuYang, Helena Seo, Mackenzi L. Prina, and Bryan W. Luikart
One out of 36 children is diagnosed annually with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the United States. Loss of function mutations in PTEN characterize PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome, a multi-system group of syndromes associated with increased risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder and increased risk of breast, thyroid, and renal cancer. One possibility to support development of targeted therapies for those with PTEN mutations is to better understand the mechanisms within commonly mutated pathways. In this study, we examine subcellular localization of PTEN and how it may affect the neuronal morphology of cells. Mechanistically, PTEN dephosphorylates PIP3 to PIP2,thereby lowering downstream AKT activation and downregulating the mTOR complexes in the P13K / AKT / mTOR pathway in the cytosol, post-synaptic density, and cytoskeleton. Within the nucleus, PTEN functions as transcriptional regulator of p53 and various checkpoints in the cell cycle, operating independently of its phosphatase activity. The P13K / AKT / mTOR pathway is largely implicated in the growth and division of cells and is highly conserved in healthy cells to regulate neuronal soma size and other growth characteristics. As demonstrated by our lab’s previous research, loss of PTEN as a negative regulator of the P13K / AKT / mTOR pathway results in increased soma size and dendritic branching in hippocampal granule neurons. This work will expand on previous research which demonstrates in mice that PTEN knockout results in neuronal overgrowth by investigating how the subcellular localization of PTEN affects its regulation of neuronal morphology via retroviral-mediated recombination of four PTEN fusion proteins (NES-PTEN, NLS-PTEN, PTEN-FBAR, and PTEN-Homer) in order to achieve spatial control over PTEN.
PTEN subcellular localization was measured using PTEN fluorescence intensity ratios in various subcellular compartments relative to other subcellular compartments and the background. In this thesis, we demonstrate success at optimizing PTEN immunostaining methodology in somas for all constructs except for PTEN-FBAR and show that PTEN-Homer and NLS-PTEN have respectively localized PTEN to the cytosol and the nucleus. Only PTEN-Homer out of all four fusion proteins achieved detectable PTEN immunostaining greater than background in dendrites and spines. Because control PTEN over-expression could not be detected above background in dendrites we were unable to determine if subcellular localization of PTEN in dendrites and spines was altered by our fusion proteins. In addition, we uncovered unexpected PTEN immunostaining in NES-PTEN mimicking that of PTEN knockout while maintaining a wildtype (WT) morphology. This poster will ponder these conclusions and brainstorm the next steps in examining other techniques for subcellular localization of PTEN.
-

Auroral Analysis: Visualizing Ionospheric Data Of The LAMP Rocket Mission
Shreya Gandhi
The Lynch Rocket Lab at Dartmouth aims to identify and study characteristics of plasma in the auroral ionosphere. Data about the ionosphere is gathered by instrumentation aboard sounding rocket missions funded by NASA. One such mission, the LAMP (Loss Through Auroral Microburst Pulsations) sounding rocket, was flown over Poker Flat, Alaska in March 2022. The rocket’s goal was to investigate the phenomenon of pulsating aurora, a unique phenomenon where aurora appear like strobe lights. My project centered around the analysis and visualization of data gathered by instrumentation aboard LAMP during its flight.
-

How Quickly Can You Find an Object? How Past Experience Speeds Attentional Selection
Lakshmi K. Jain, Kevin Ortego, and Viola Störmer
-

Exploring high-order network dynamics in brains and stock markets
Kunal Jha, Daniel Carstensen, Ansh Patel, and Jeremy R. Manning
Human cognition is fundamentally a network phenomenon: our thoughts, sense of self, and our other brain functions reflect coordinated interactions between our brain’s constituent cells and systems. These interactions change over time alongside our experiences, goals, and internally driven thoughts. Whereas early work on neural decoding attempted to infer internal representations by considering univariate (single region) or multivariate (patterns of regions) activity patterns, later studies have treated patterns of network interactions as a core unit of neural representation and computation. The field has also started to consider the potential role of higher order network interactions. If two regions, A and B, adjust their interactions over time in response to ongoing task demands, and two other regions, C and D, also adjust their interactions over time, second order interactions denote potential associations between the A-B interactions and C-D interactions. In the general case, order n interactions reflect associations between networks of order n - 1 interactions. In a recent study, our team found that meaningful high-order interactions between brain networks spontaneously emerge during deep cognitive processing, and they spontaneously dissociate during less demanding or focused cognition. Here we wondered if other sorts of networks might show a similar pattern. We applied a model of high-order network dynamics to a financial dataset comprising historical stock quotes from the S&P 500. We estimated which orders of interactions were most reflective of the “true” system dynamics by using different sets of features (made of network patterns at different orders) to predict future states of the market. We compared how informative different orders of interactions in financial data were at predicting future states of the S&P 500 to how informative different orders of brain interactions were in different experimental conditions in a neuroscientific dataset. We found that, like biological brains, financial markets appear to contain meaningful high-order interactions that change over time with market conditions, important historical events, and so on.
-

Site-directed mutagenesis on C252 and H734 from adhE in a shuttle vector
Meghan Kerfoot, Angel Pech, and Daniel Olson
-

Hanover Underground: Mapping the Subsurface of Dartmouth's Campus
Grace E. Mendolia and Sophie Lewis
My project involved mapping the sediments of Dartmouth's campus in order to determine the best locations for efficient geothermal drilling as well as to better understand the glacial history of Hanover.
-

Bifurcation structure in Auroral radio emissions
Annabelle E. Niblett and James W. LaBelle Dr.
The northern lights, or aurora borealis, are best known for the beautiful optical displays they present in the polar atmosphere. It is less widely known, but the northern lights also emit various types of radio waves which cannot be seen but can be detected with sensitive instruments. These radio waves provide insights into the physics of the aurora. One type of auroral radio emission, called auroral "roar" occurs on frequencies near 3 MHz, somewhat above the highest AM radio frequencies. On some occasions, this radio emission occurs on two closely space frequencies rather than a single frequency band, a phenomenon called a doublet structure. The explanation for these doublet structures is not known. The structure of the electron density in the ionosphere may play a role. The WISP project would entail cataloguing a large number of examples for the first time, in order to determine the distributions of the frequencies and the gap between them. This information may provide a test of whether ionospheric density structure can explain the phenomenon.
-

Cryogel Scaffold Mediated Bone Regeneration for Improved Metastatic Bone Disease Treatments
Annika Nikhar, Peter Bertone, Eric Henderson, and Katherine Hixon
Nearly 50% of cancers originating in organs such as the breast, prostate, and lungs spread to the skeleton. Typical metastatic bone disease (MBD) treatments include radiation and surgery; however, these interventions often bear adverse effects including infection, soft-tissue damage, and osteoporosis. Thus, improved bone regeneration could revolutionize MBD treatments where cryogel scaffolds offer a viable option. This project investigates cryogel incorporation with current radiotherapy (RT) treatments following bone tumor resection. Alternatively, FLASH RT irradiates tissue within ultra-short durations at high doses, reducing tissue toxicity and treatment time. However, the effects of FLASH on the material properties remains unclear. Cryogels were hydrated in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), mimicking in vivo conditions, and exposed to conventional or FLASH RT at varying clinically-relevant fractionated doses. All samples were then assessed for translation potential (i.e., porosity, mechanical integrity, and swelling kinetics). To determine whether hydrated cryogels exhibited property changes due to effects of irradiation or potential degradation from PBS, non-irradiated control cryogels were immersed in PBS for parallel fractionated doses. We hypothesized that hydrating cryogels in PBS during RT exposures will not affect material physical properties.
-

Magnetic Measurements of Ancient Sedimentary Processes and Redox Conditions in the Grand Canyon
Abigail Paquette and Sarah Slotznick
-
Distinguishing the role of dorsal precuneus in visual perception and memory
Nandhini Parthasarathy, Adam Steel, and Caroline E. Robertson
-

Discovering Dwarf Galaxies Around Low Mass Galaxies
Madeleine Saraisky and Bo Farnell
The goal of this project is to discover satellite dwarf galaxies around low mass galaxies. These dwarf galaxies are important to study because a large portion of the galaxies' mass is made up of dark matter. Dwarf galaxies are the smallest, oldest, faintest, and most dark matter dominated systems, and as such, are extremely important for the studies of galaxy formation and dark matter. The satellite dwarves being identified around low mass galaxies are a specific type of dwarf galaxy known as low surface brightness galaxies, or LSBGs. LSBGs are a very diffuse type of dwarf galaxy that emit much less light per unit area compared to other galaxies because of their low density of stars. These galaxies are discovered through a systematic visual search of regions around target hosts (low mass galaxies). This search is conducted using images from the Legacy survey, composed of data from three separate imaging projects. Theories predict that there should be 4-5 LSBGs around each low mass galaxy, so findings from this project could either work to support or refute this theory, contributing either way to the study of LSBGs and dark matter.
-

The Relationship Between Visual Working Memory and Fluid Intelligence
Kaira Kuo Shlipak, Yong Hoon Chung, and Viola Stoermer
Carole Folt Research Scholarship Award
The goal of this project is to investigate the relationship between fluid intelligence and visual working memory capacity. Fluid intelligence refers to the ability to solve abstract problems and is one of the most important constructs in psychological research. Interestingly, visual working memory– the limited ability to hold visual information in an active state for short periods of time– has been shown to strongly correlate with measures of fluid intelligence. However, the mechanisms underlying this relation are still unclear. My research investigates how broad the relationship between working memory capacity and intelligence measures are, and whether it generalizes to more naturalistic tasks. Specifically, recent research has shown that working memory capacity is increased when remembering real-world objects relative to simple visual features (i.e., colored squares or oriented lines) that have been traditionally used. I propose to test whether the capacity to remember these real-world objects also correlates with measures of fluid intelligence. The findings from this study have important implications for how fluid intelligence measures relate to different working memory tasks, and in particular to how we use working memory in more naturalistic settings: when we are trying to remember real-world objects, and not just simple geometric shapes. -

Effects Of Daylight On Student Well-being
Sathya Thenappan
While existing literature predominantly deals with the impact of daylight on adults in general and more specifically at the workplace, less is known about its impact on the college student demographic and daylight exposure levels at college residences. Given its considerable impact on both the physical and mental well-being of individuals, daylight has been used in the treatment of an assortment of diseases from seasonal affective disorder to depression. With college students constituting the majority of today’s people who suffer from mental health issues in society, uncovering the link between daylight exposure and its impact on the physical and mental wellbeing of these students specifically, will enable harnessing of the benefits of daylight, and potentially alleviate the ongoing mental health crisis in college populations. In this study, I use a series of regression analyses and instrumental variable estimations to ascertain the link between exposure to daylight and its impact on both the physical (SF-36 scale), and mental (PHQ-9, GAD-7, and PSQI scales) well-being of a cohort of Dartmouth undergraduates (N=344), who vary in terms of their daylight exposure levels. In particular, I differentiate between two scales of daylight exposure levels, namely a subjective daylight exposure scale which reflects college students’ self-assessment of their level of daylight exposure, and an objective daylight exposure scale that reflects a more objective assessment of their level of daylight exposure within their college housing. Results provide some support for the hypotheses that higher levels of daylight exposure lead to both better mental and physical health outcomes. However, further instrumental variable estimation using the objective daylight exposure scale as an instrument proves that this estimated causal effects are statistically insignificant or imprecise, despite controlling for confounding factors. Ultimately, there is not enough evidence to support a causal relationship between the daylight exposure treatment and the health outcomes. This does not necessarily mean that there is no causal effect between daylight exposure and the physical and mental well-being of college students, but rather, that the available data and methods used in this study do not provide convincing enough evidence to prove causation.
-
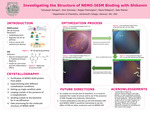
Investigating the Structure of NEMO-I65M Binding with Shikonin
Tanyawan Wongsri, Amy Kennedy, Pepper Pennington, Maria Pellegrini, and Dale Mierke
This poster summarizes the results of a protein crystallography investigation between the NEMO-I65M mutant and small molecule Shikonin (SHK).
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.




